Was ist Pathologie?

Das Fundament moderner Diagnostik.

Pioneering Pathology - Leading the Future of Diagnosis with Precision and Innovation in Science and Teaching
Pathology is a central field of medicine that deals with the detection, classification, and analysis of diseases. With the aim of identifying the exact cause of a disease, we lay the foundation for optimal treatment. Only with a solid diagnosis can the appropriate treatment of patients begin—whether in cancer research, chronic infections and inflammations, autoimmune diseases, or other complex clinical pictures.
We examine:
In rare cases, the institute performs what is known as a clinical autopsy (approximately 300 autopsies per year compared to 135,000 patient samples per year). A clinical autopsy is performed for various reasons:
Overall, clinical pathology (99% of activities) and clinical autopsy (1% of activities) play a central role in understanding diseases and improving medical care. Autopsies also contribute to medical quality assurance and teaching, but are not the focus of today's work in pathology.



Using rapid cut diagnostics, pathologists make a diagnosis during an ongoing operation (within a few minutes) that directly influences the course of the surgical procedure (e.g., treatment of malignant tumors).
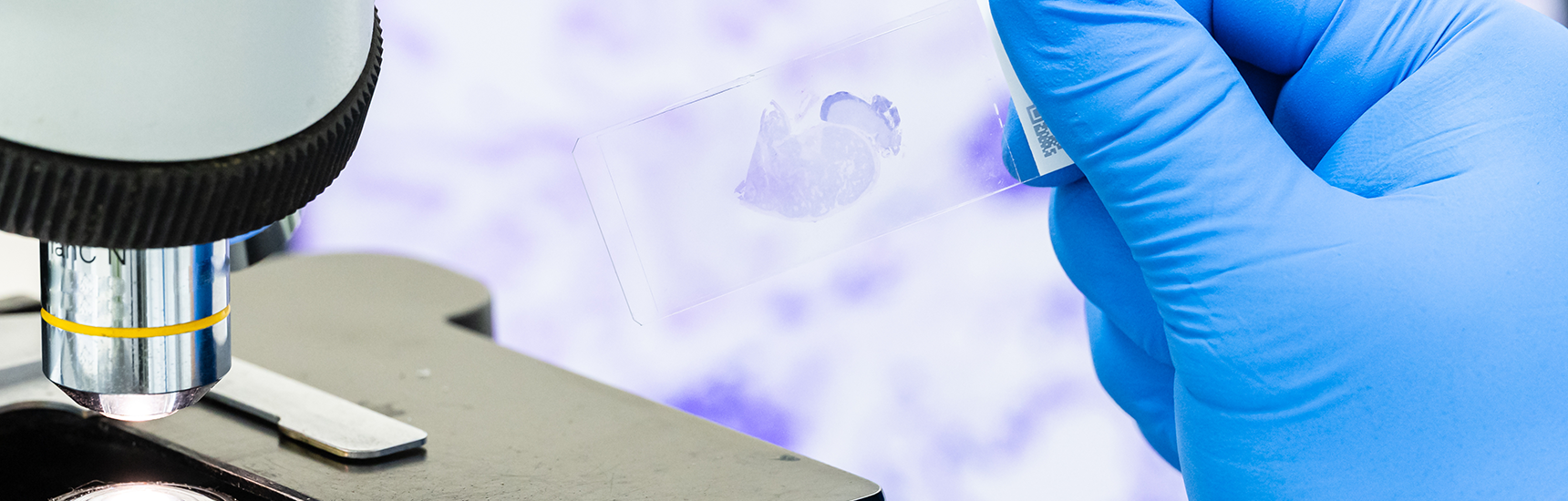
With cytopathological diagnostics, cells from organs, body cavities and body fluids are harvested using swabs, sedimentation or needle biopsy and then examined. The main goals are detection and early diagnosis of malignant disease.
An autopsy is also a medical diagnostic activity through which the clinical diagnosis can be checked or confirmed and the efficiency of diagnostic and therapeutic procedures is estimated.
Today many examinations must be completed with immunohistochemical procedures and the additional use of methods of molecular pathology (biochemistry, molecular genetics).

Tests conducted at the Diagnostic and Research Institute of Pathology and their evaluation by pathologists in the context of medical diagnosis serve as the basis for diagnostics and decisions about therapy and are also an integral component in the monitoring of therapy and disease progression.
The structure of the required processes from the perspective of IVD-VO 2017/746 and EN ISO 15189 enables top-level reporting.
Internal and external quality management measures guarantee that processes are conducted under standardized conditions, the professional development of staff is ongoing and test results are continuously monitored. The regular evaluation of key performance indicators significantly contributes to a constant improvement in quality. The aim is to achieve accreditation according to EN ISO 15189 as an independent confirmation of our efforts and competence.





